What Are The Reactants Of Cellular Respiration? Breaking It Down For You
Alright, let’s dive right into it—what are the reactants of cellular respiration? If you’re scratching your head trying to figure out what’s going on inside your body’s energy production factory, you’ve come to the right place. Cellular respiration is basically the process where your cells turn glucose and oxygen into energy that keeps you alive and kicking. And the reactants? Well, they’re the starting materials for this whole energy-making magic show.
Think of it like cooking a meal. You need ingredients, right? In this case, the ingredients are glucose and oxygen. These two team up inside your cells to create energy, carbon dioxide, and water. It’s like a recipe for life, and without these reactants, the whole system would fall apart. So, if you’re curious about how your body fuels itself, stick around because we’re about to break it down step by step.
Now, before we go too deep, let’s set the stage. Cellular respiration isn’t just some random process happening in the background. It’s essential for everything you do, from running a marathon to just sitting there scrolling through your phone. Understanding the reactants and how they work together can give you a whole new appreciation for how your body functions. Ready to learn more? Let’s get started.
Understanding Cellular Respiration: A Quick Overview
Cellular respiration is kind of like the powerhouse of your body. It’s the process where cells convert nutrients into usable energy, and it happens in almost every living organism. The main goal here is to produce ATP, which is like the currency of energy in your cells. But to make ATP, you need reactants, and that’s where glucose and oxygen come in.
Here’s the deal: when you eat food, your body breaks it down into glucose, which is a type of sugar. Meanwhile, you’re breathing in oxygen from the air around you. These two substances meet up inside your cells, specifically in the mitochondria, which is often called the "powerhouse of the cell." Together, they go through a series of reactions to produce energy, along with some byproducts like carbon dioxide and water.
So, why is this important? Well, without cellular respiration, your cells wouldn’t have the energy they need to function. It’s like trying to drive a car without fuel. Everything in your body, from your brain to your muscles, relies on this process to keep things running smoothly. And it all starts with those two key reactants: glucose and oxygen.
Why Are Reactants So Important?
Reactants are basically the raw materials that kickstart the whole process. In the case of cellular respiration, glucose provides the energy source, while oxygen acts as the helper that makes everything work. Without these two, the reaction can’t happen, and your cells wouldn’t be able to produce ATP.
- Glucose: This is the sugar molecule that your body breaks down to release energy. It comes from the food you eat, especially carbohydrates.
- Oxygen: This gas is essential for the process to work efficiently. It helps break down glucose completely, producing more energy than if oxygen wasn’t involved.
Think of it like a fire. To start a fire, you need fuel (like wood) and oxygen. Without either one, the fire won’t burn. Similarly, cellular respiration needs both glucose and oxygen to produce energy effectively.
What Are the Reactants of Cellular Respiration? The Main Players
Alright, let’s get specific. The reactants of cellular respiration are glucose and oxygen. These two substances are the stars of the show, and they work together in a series of steps to produce energy. Let’s break it down:
Glucose: The Energy Source
Glucose is a type of sugar that your body gets from the food you eat. When you consume carbohydrates, your digestive system breaks them down into glucose, which is then transported to your cells through the bloodstream. Inside the cells, glucose is broken down during cellular respiration to release energy.
Here’s the cool part: glucose is packed with energy. It’s like a battery that powers your cells. When it’s broken down, it releases that energy in the form of ATP, which your cells can use to do all sorts of things, like contracting muscles or sending signals through your nerves.
Oxygen: The Helper
Oxygen is the other key reactant in cellular respiration. You breathe it in from the air, and it’s transported to your cells through your bloodstream. Once it gets there, it helps break down glucose completely, producing more energy than if oxygen wasn’t involved.
Without oxygen, the process would be incomplete, and your cells would only be able to produce a fraction of the energy they need. This is why aerobic respiration (with oxygen) is so much more efficient than anaerobic respiration (without oxygen).
The Steps of Cellular Respiration: Where the Magic Happens
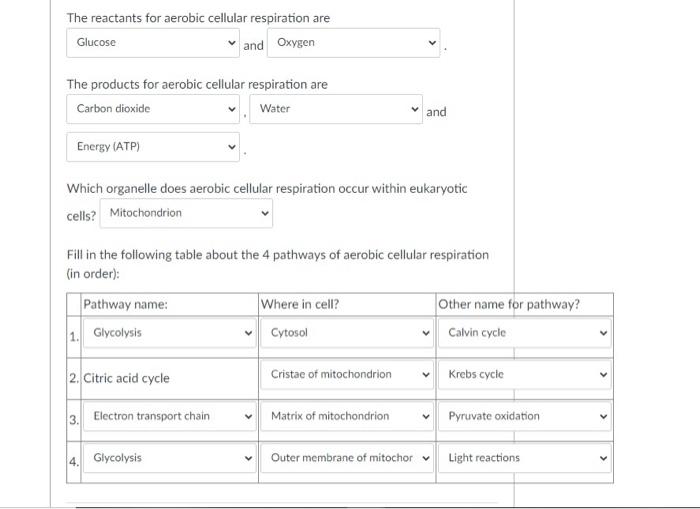
Now that we know the reactants, let’s talk about how they actually work together. Cellular respiration happens in three main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle (also called the citric acid cycle), and the electron transport chain. Each stage plays a crucial role in breaking down glucose and producing energy.
Glycolysis: Breaking Down Glucose
Glycolysis is the first step in cellular respiration, and it happens in the cytoplasm of the cell. During this process, glucose is split into two molecules of pyruvate, releasing a small amount of energy in the form of ATP. This step doesn’t require oxygen, so it can happen even if oxygen isn’t available.
The Krebs Cycle: Turning Pyruvate into Energy
Next up is the Krebs cycle, which takes place in the mitochondria. Here, the pyruvate molecules from glycolysis are further broken down, releasing more energy in the form of ATP, as well as carbon dioxide and water. This step requires oxygen, which is why it’s part of aerobic respiration.
The Electron Transport Chain: Producing the Most Energy
The final step is the electron transport chain, which also happens in the mitochondria. This is where the majority of ATP is produced. Oxygen plays a crucial role here, as it helps capture the electrons that are being transported through the chain. Without oxygen, this step wouldn’t happen, and your cells wouldn’t be able to produce enough energy to survive.
Why Is Cellular Respiration So Important?
Cellular respiration is the process that keeps you alive. It’s how your cells produce the energy they need to function, and it happens in every living organism. Without it, your body wouldn’t be able to do anything, from thinking to moving to breathing. It’s like the engine that powers your entire body.
Here’s why it matters:
- Energy Production: ATP is the energy currency of your cells, and cellular respiration is how it’s produced. Without ATP, your cells wouldn’t have the energy they need to function.
- Efficient Use of Resources: By breaking down glucose and oxygen completely, cellular respiration ensures that your body gets the most energy possible from the food you eat.
- Waste Removal: The byproducts of cellular respiration, like carbon dioxide and water, are easily removed from your body through breathing and sweating.
How Does Cellular Respiration Affect Your Daily Life?
You might not think about cellular respiration very often, but it affects every single thing you do. Whether you’re running a marathon or just sitting on the couch watching TV, your cells are hard at work producing energy through this process. Here are a few ways it impacts your daily life:
Exercise and Energy
When you exercise, your muscles need more energy, which means your cells need to produce more ATP. This is where cellular respiration really kicks into high gear. Your body increases its oxygen intake to meet the demand, and your cells work overtime to break down glucose and produce energy.
Metabolism and Weight Management
Your metabolism is essentially the rate at which your body breaks down food into energy. Cellular respiration is a big part of this process, and understanding how it works can help you manage your weight more effectively. For example, if you’re trying to lose weight, you might focus on increasing your oxygen intake through exercise to boost your metabolism.
Common Misconceptions About Cellular Respiration
There are a few common misconceptions about cellular respiration that we should clear up. For example, some people think that it only happens in animals, but that’s not true. Plants also undergo cellular respiration to produce energy, although they get their glucose from photosynthesis instead of food.
Another misconception is that cellular respiration is the same as breathing. While breathing is an important part of the process (since it’s how you get oxygen into your body), it’s not the same thing. Cellular respiration happens inside your cells, while breathing is just the process of moving air in and out of your lungs.
The Role of Reactants in Cellular Respiration
Let’s circle back to the reactants for a moment. Glucose and oxygen are the two key substances that make cellular respiration possible. Without them, the process wouldn’t happen, and your cells wouldn’t be able to produce energy. Here’s a quick recap of their roles:
- Glucose: Provides the energy source that gets broken down to release ATP.
- Oxygen: Helps break down glucose completely, producing more energy and ensuring the process is efficient.
It’s a pretty simple concept when you break it down, but the impact is huge. These two substances work together to keep your body running smoothly, and they’re essential for life as we know it.
How Can You Support Cellular Respiration?
If you want to support your body’s cellular respiration process, there are a few things you can do. First, make sure you’re eating a balanced diet that provides plenty of glucose from healthy sources like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Second, stay active to increase your oxygen intake and improve your overall health. And finally, take care of your mitochondria by avoiding toxins and stress, which can damage these important cellular structures.
Conclusion: Why Cellular Respiration Matters
So, there you have it. The reactants of cellular respiration are glucose and oxygen, and they work together to produce the energy your body needs to function. This process is essential for life, and understanding how it works can give you a whole new appreciation for how your body keeps you alive and kicking every single day.
Now that you know the basics, why not take a moment to reflect on how amazing your body really is? And if you found this article helpful, don’t forget to share it with your friends and family. Who knows? You might just inspire someone else to learn more about the incredible processes happening inside their own body.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Cellular Respiration: A Quick Overview
- Why Are Reactants So Important?
- What Are the Reactants of Cellular Respiration? The Main Players
- The Steps of Cellular Respiration: Where the Magic Happens
- Why Is Cellular Respiration So Important?
- How Does Cellular Respiration Affect Your Daily Life?
- Common Misconceptions About Cellular Respiration
- The Role of Reactants in Cellular Respiration
- How Can You Support Cellular Respiration?
- Conclusion: Why Cellular Respiration Matters


Detail Author:
- Name : Branson Medhurst
- Username : wolff.meghan
- Email : tiara12@mclaughlin.com
- Birthdate : 1989-04-16
- Address : 7999 Wintheiser Grove Casperhaven, KS 55090-8533
- Phone : 603.383.4665
- Company : Becker LLC
- Job : Physician Assistant
- Bio : Illum maiores unde assumenda perferendis veniam. Occaecati architecto molestiae et recusandae itaque. Reprehenderit omnis fugit dolorum blanditiis et illum et. Labore qui et dicta ipsa.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/ayden1727
- username : ayden1727
- bio : Et iure nemo possimus. Nihil ut ducimus tempora. Explicabo harum incidunt beatae vel.
- followers : 1402
- following : 937
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/aydenschumm
- username : aydenschumm
- bio : Dolores autem quis deserunt vel saepe sit quia. Odit laboriosam iure fuga.
- followers : 3662
- following : 843