Unraveling The Secrets Of Carbohydrate Monomer: Your Ultimate Guide
Ever wondered what makes carbohydrates tick? Let's dive into the fascinating world of carbohydrate monomers, the building blocks of all things sugary and starchy. From powering your morning jog to fueling your brain during those late-night study sessions, these tiny molecules play a massive role in our lives. But what exactly are they, and why do they matter so much?
Carbohydrates, often referred to as carbs, are one of the primary sources of energy for living organisms. But did you know that their story begins with something called a carbohydrate monomer? These little guys are like the LEGO bricks of the carbohydrate world—simple yet essential. Understanding them can give you a deeper appreciation for how your body generates energy and maintains balance.
In this guide, we'll break down everything you need to know about carbohydrate monomers. From their structure and function to their role in health and nutrition, we’ve got you covered. So grab a snack—preferably a carb-heavy one—and let’s get started!
Table of Contents
- What is a Carbohydrate Monomer?
- Types of Carbohydrate Monomers
- Structure and Function of Carbohydrate Monomers
- Glycogen and Energy Storage
- Carbohydrate Monomer in Your Diet
- Health Impacts of Carbohydrate Monomers
- Monosaccharides vs Polysaccharides
- Enzymatic Breakdown of Carbohydrates
- Recent Research on Carbohydrate Monomers
- Conclusion: Why Carbohydrate Monomers Matter
What is a Carbohydrate Monomer?
A carbohydrate monomer, also known as a monosaccharide, is the simplest form of carbohydrate. Think of it as the basic unit that builds up more complex carbs like disaccharides and polysaccharides. These little molecules are sweet, colorless, and water-soluble, making them perfect for quick energy bursts.
Now, here's the kicker—monosaccharides are super versatile. They’re not just about giving you a sugar rush; they also play crucial roles in cellular processes, structural support, and even communication between cells. So yeah, they’re kind of a big deal.
Key Characteristics
- Simple sugars with the general formula (CH2O)n
- Examples include glucose, fructose, and galactose
- Found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy products
Types of Carbohydrate Monomers
Not all carbohydrate monomers are created equal. There are several types, each with its own unique properties and functions. Let’s take a closer look:
Glucose: The Energy Powerhouse
Glucose is arguably the most famous monosaccharide out there. It’s the main source of energy for your body and brain. When you eat carbs, your digestive system breaks them down into glucose, which is then absorbed into your bloodstream. This is why people talk about "blood sugar" levels—it’s all about glucose!
Fructose: The Sweet Tooth’s Best Friend
Fructose is another big player in the monosaccharide game. Found naturally in fruits and honey, this sugar is what gives them their sweetness. However, unlike glucose, fructose is metabolized differently in the liver, which has sparked some interesting debates in the nutrition world.
Galactose: The Quiet Partner
Galactose often flies under the radar, but it’s just as important as its more famous siblings. It pairs up with glucose to form lactose, the sugar found in milk and dairy products. Without galactose, your morning cereal wouldn’t be nearly as tasty!
Structure and Function of Carbohydrate Monomers
Understanding the structure of carbohydrate monomers is key to appreciating their function. Monosaccharides are typically composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms arranged in a ring-like structure. This arrangement allows them to interact with enzymes and other molecules in fascinating ways.
For example, glucose can exist in two forms: alpha and beta. These subtle differences in structure can affect how the molecule is absorbed and utilized by the body. Cool, right?
Functions Beyond Energy
- Cell signaling and communication
- Structural support in cell walls
- Storage of energy in the form of glycogen
Glycogen and Energy Storage
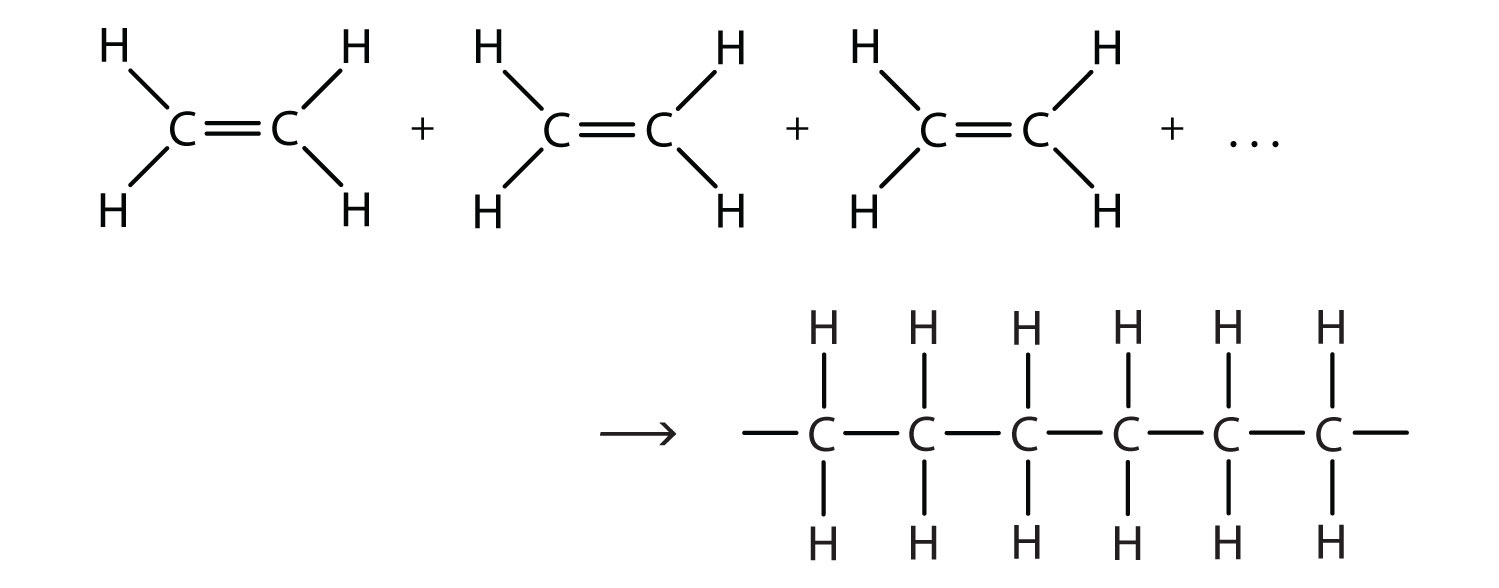
When your body has more glucose than it needs, it doesn’t just throw it away. Instead, it stores it in the form of glycogen, a polysaccharide made up of many glucose monomers. Glycogen is like your body’s emergency energy fund, ready to kick in when you need a quick boost.
Interestingly, glycogen is stored primarily in the liver and muscles. This strategic placement ensures that energy is readily available wherever it’s needed most. So next time you hit the gym, remember that glycogen is your secret weapon!
Carbohydrate Monomer in Your Diet
Now that we know how important carbohydrate monomers are, let’s talk about where you can find them in your diet. Fruits, vegetables, grains, and dairy products are all excellent sources of monosaccharides. But not all carbs are created equal, and the quality of your carbohydrate intake matters just as much as the quantity.
For example, whole grains and fruits provide a steady stream of energy, while refined sugars can cause rapid spikes and crashes in blood sugar levels. This is why nutritionists often recommend focusing on complex carbs rather than simple ones.
Top Sources of Monosaccharides
- Apples
- Carrots
- Oats
- Milk
- Honey
Health Impacts of Carbohydrate Monomers
While carbohydrate monomers are essential for energy, they can also have significant impacts on your health. Consuming too many simple sugars, for instance, has been linked to obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic disorders. On the flip side, a balanced intake of complex carbs can support weight management, improve brain function, and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
It’s all about moderation and making smart choices. So instead of reaching for that candy bar, why not grab an apple or a handful of nuts? Your body will thank you later.
Recent Studies
Research continues to uncover new insights into the role of carbohydrate monomers in health. For example, a study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that diets rich in whole grains were associated with lower risks of heart disease and type 2 diabetes. Meanwhile, another study highlighted the potential benefits of fructose in athletic performance, provided it’s consumed in moderation.
Monosaccharides vs Polysaccharides
While we’ve been focusing on monosaccharides, it’s worth noting that they’re just one piece of the carbohydrate puzzle. Polysaccharides, like starch and cellulose, are made up of many monosaccharides linked together. These complex carbs take longer to break down, providing a more sustained source of energy.
Think of it like this: monosaccharides are like fast food—they give you a quick hit of energy. Polysaccharides, on the other hand, are like a slow-cooked meal—they keep you going for hours.
Which One Should You Choose?
The answer depends on your goals and lifestyle. If you need a quick energy boost, monosaccharides are the way to go. But for long-term energy and overall health, polysaccharides are the better choice. As always, balance is key.
Enzymatic Breakdown of Carbohydrates
Before your body can use carbohydrate monomers, it needs to break them down from more complex forms. This process involves a variety of enzymes, each with its own specific role. For example, amylase breaks down starch into maltose, while lactase breaks down lactose into glucose and galactose.
Interestingly, some people have genetic variations that affect their ability to produce certain enzymes. This is why lactose intolerance is so common—many adults stop producing lactase after childhood, making it difficult for them to digest dairy products.
Recent Research on Carbohydrate Monomers
The field of carbohydrate research is constantly evolving, with new discoveries being made all the time. Recent studies have explored everything from the role of monosaccharides in gut health to their potential applications in biofuels and medicine.
One particularly exciting area of research involves using carbohydrate monomers to develop new treatments for diseases like cancer and Alzheimer’s. By targeting specific sugar molecules, scientists hope to disrupt the processes that allow these diseases to thrive.
Conclusion: Why Carbohydrate Monomers Matter
From powering your daily activities to supporting complex biological processes, carbohydrate monomers are truly the unsung heroes of the nutrition world. By understanding their structure, function, and role in health, you can make more informed choices about your diet and overall well-being.
So next time you reach for a snack, take a moment to appreciate the tiny but mighty monosaccharides that make it all possible. And don’t forget to share this article with your friends—they might learn something new too!
Got questions or comments? Drop them below, and let’s keep the conversation going. Who knows—maybe you’ll discover something sweet along the way!


Detail Author:
- Name : Miss Lulu Heidenreich PhD
- Username : yhermiston
- Email : jarrell.bahringer@heller.com
- Birthdate : 2004-08-18
- Address : 571 Micah Trafficway Karolannhaven, PA 44062
- Phone : +13217485295
- Company : Dickinson PLC
- Job : Preschool Teacher
- Bio : Optio eveniet iste et quos quas. Minus quo sunt et similique tenetur unde. Vel eos ratione officia at et dolor.
Socials
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/stehry
- username : stehry
- bio : Expedita autem repellendus ut laboriosam dolores exercitationem maxime. Dolorem aut enim sit in necessitatibus in nihil. Facere itaque non qui ut mollitia.
- followers : 2407
- following : 2581
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/yoshiko3151
- username : yoshiko3151
- bio : Quibusdam doloremque molestiae tempore enim.
- followers : 152
- following : 583
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/yoshiko8166
- username : yoshiko8166
- bio : Quo vel repudiandae sit ut magnam esse.
- followers : 1061
- following : 283