California Precipitation Totals: Unveiling The Rainfall Secrets Of The Golden State
California precipitation totals have been a hot topic among weather enthusiasts, farmers, scientists, and policy makers for years. The state’s unique geography and climate patterns make rainfall a critical factor in determining water availability, agricultural success, and even wildfire risks. But what exactly drives these precipitation levels? Let’s dive into the fascinating world of California’s weather and uncover the secrets behind its rainfall patterns.
Imagine California as a giant puzzle where every piece plays a role in shaping its environment. From the towering Sierra Nevada mountains to the coastal fog that blankets the shoreline, the state’s diverse landscapes influence how much rain falls each year. Understanding these dynamics isn’t just about satisfying curiosity; it’s essential for planning and managing resources effectively.
Whether you’re a local resident wondering if this year will bring relief from drought or a researcher studying climate trends, this article has got you covered. We’ll explore everything from historical data to current projections, shedding light on why California’s precipitation totals matter so much. So grab your coffee, settle in, and let’s get started!
Understanding California Precipitation Totals
When people talk about California precipitation totals, they’re referring to the amount of rainfall and snowfall measured across the state over specific periods. These measurements are critical because they determine how much water is available for drinking, farming, and other essential uses. But here’s the thing—California’s weather isn’t as predictable as you might think.
The state experiences a Mediterranean climate, meaning most of its rain falls during the winter months while summers remain dry. This seasonal variation creates challenges for water management, especially during drought years when precipitation totals dip below average. To complicate matters further, climate change is altering these patterns, making extreme weather events more frequent.
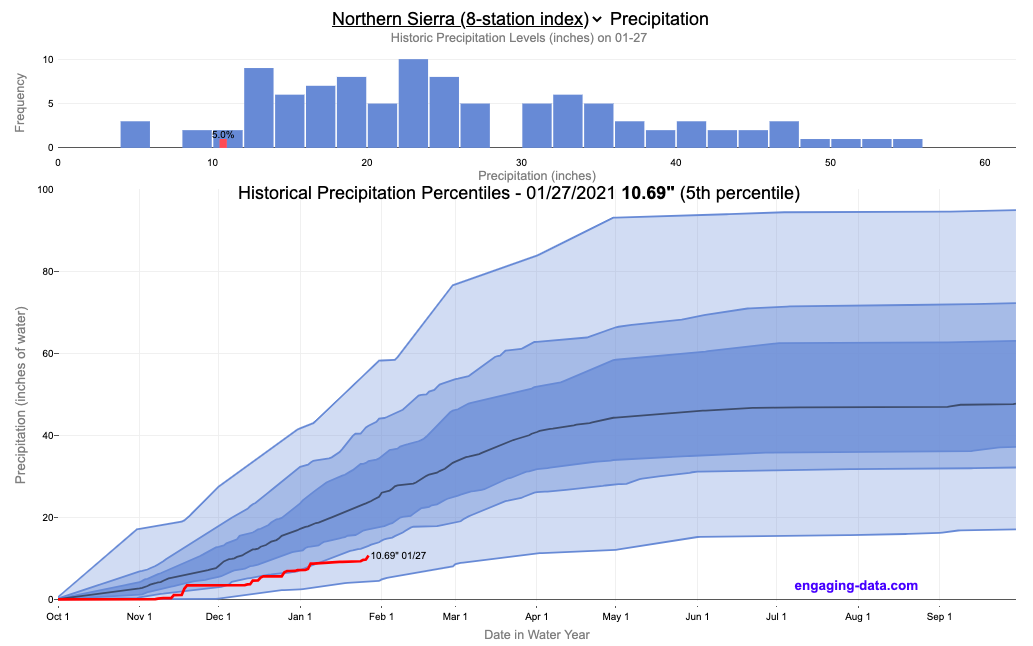
For instance, recent years have seen some of the wettest and driest seasons on record. In 2016-2017, Northern California experienced record-breaking rainfall, filling reservoirs to capacity. Fast forward to 2021, and the state faced one of its worst droughts in decades. These fluctuations highlight the importance of understanding and tracking precipitation trends.
Factors Influencing California Precipitation Totals
Several factors contribute to California’s precipitation totals, each playing a unique role in shaping the state’s weather. Below are some key influencers:
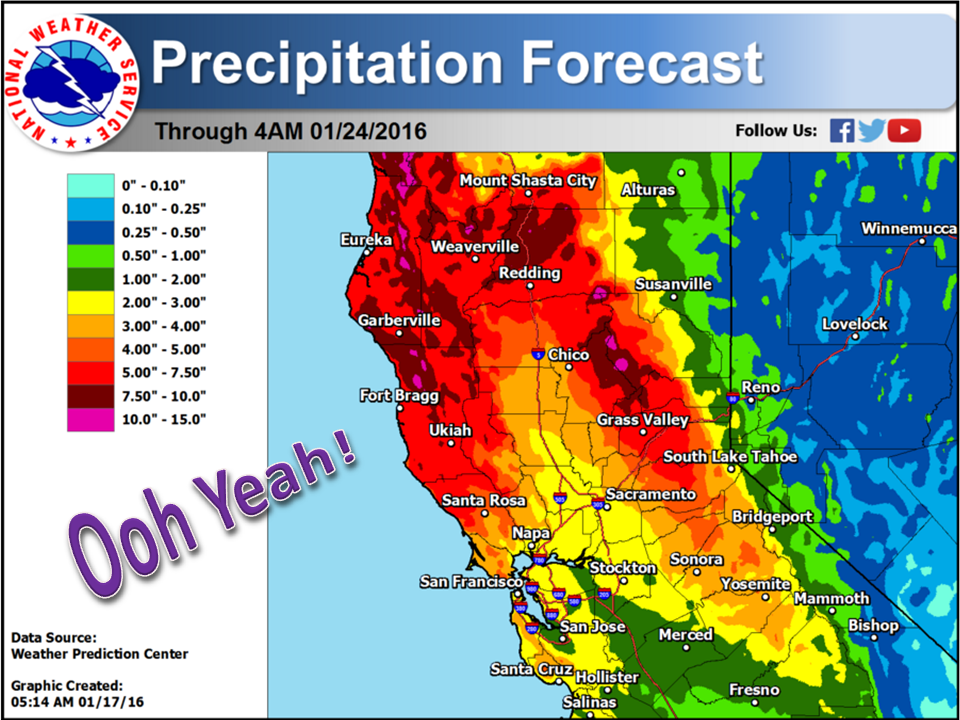
- Atmospheric Rivers: These massive bands of moisture streaming across the Pacific Ocean deliver much of California’s rainfall. When they make landfall, they can bring torrential rains and heavy snowfall, especially in mountainous regions.
- El Niño and La Niña: These climate phenomena significantly impact precipitation patterns. El Niño often brings wetter conditions to Southern California, while La Niña can lead to drier-than-average winters.
- Topography: California’s varied landscape, including its coastal ranges and inland mountains, affects how precipitation is distributed. Areas on the windward side of mountains tend to receive more rain, while leeward sides experience rain shadows.
Understanding these factors helps scientists predict future precipitation trends and develop strategies to mitigate the impacts of drought and flooding.
Historical Perspective on California Precipitation
Looking back at historical data provides valuable insights into California’s precipitation patterns. Records show that the state has always experienced significant variability in rainfall, with wet and dry periods alternating over time. For example, the early 20th century saw several years of above-average precipitation, followed by prolonged droughts in the mid-1920s.
One of the most notable events was the Great Flood of 1862, which submerged vast areas of California under water. This extreme weather event serves as a reminder of the state’s vulnerability to natural disasters driven by intense rainfall. On the flip side, the Dust Bowl era of the 1930s highlighted the consequences of prolonged drought, impacting agriculture and livelihoods across the region.
Current Trends in California Precipitation Totals
Recent years have brought new challenges and opportunities in terms of California precipitation totals. Climate change is reshaping the state’s weather patterns, leading to more intense storms and longer dry spells. Scientists predict that these trends will continue, with potentially severe implications for water resources.
One concerning trend is the increasing frequency of "whiplash" events, where extreme wet and dry conditions occur back-to-back. This phenomenon makes it difficult for water managers to plan and allocate resources effectively. Additionally, rising temperatures are causing more precipitation to fall as rain rather than snow, reducing the snowpack that traditionally acts as a natural reservoir.
Regional Variations in Precipitation
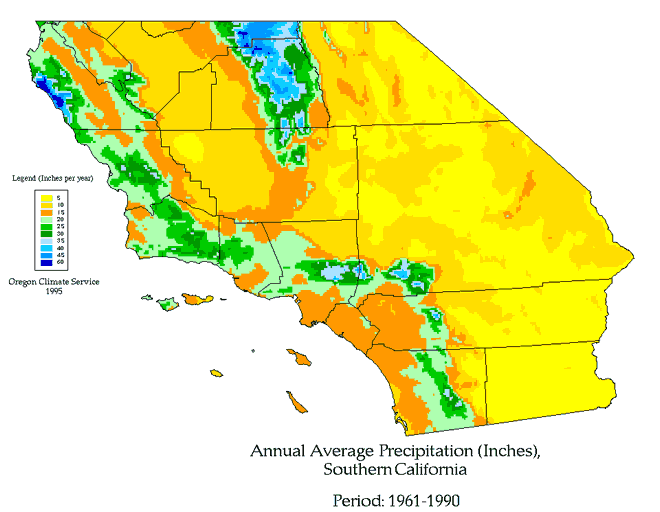
California’s large size and diverse geography result in significant regional variations in precipitation totals. While Northern California typically receives more rainfall due to its proximity to atmospheric rivers, Southern California often struggles with limited moisture. Coastal areas benefit from marine influences, while inland regions face hotter, drier conditions.
These differences highlight the need for localized approaches to water management. For example, urban areas like Los Angeles rely heavily on imported water to meet their needs, while rural communities depend on local sources such as groundwater and surface water.
Impact of Precipitation on Agriculture
Agriculture is a cornerstone of California’s economy, accounting for a significant portion of the state’s GDP. However, the industry’s success hinges on reliable access to water, making precipitation totals a critical factor. Farmers depend on both natural rainfall and irrigation systems to grow crops, but prolonged droughts can severely impact production.
In recent years, many growers have adopted innovative techniques to conserve water, such as precision irrigation and drought-resistant crop varieties. Despite these efforts, the unpredictability of precipitation remains a major challenge. For instance, the 2012-2016 drought forced many farmers to fallow fields and reduce livestock herds, resulting in billions of dollars in losses.
Water Management Strategies
Managing water resources effectively requires a multi-faceted approach that considers both short-term needs and long-term sustainability. Some of the strategies currently being implemented include:
- Building new reservoirs and expanding existing ones to capture excess rainfall during wet years.
- Promoting water recycling and reuse programs to reduce reliance on freshwater sources.
- Encouraging conservation practices among residents and businesses to minimize waste.
These initiatives aim to create a more resilient water system capable of withstanding the impacts of climate change and population growth.
Climate Change and Future Projections
As global temperatures continue to rise, California’s precipitation patterns are expected to undergo further changes. Models suggest that the state may see fewer but more intense storms, leading to increased flood risks. At the same time, hotter temperatures will accelerate evaporation, reducing the amount of water available for use.
Scientists warn that these shifts could exacerbate existing water challenges, particularly in areas already prone to drought. To prepare for this uncertain future, policymakers must prioritize investments in infrastructure, research, and education. By fostering collaboration between stakeholders, California can build a water-smart society ready to face whatever comes its way.
Adapting to Changing Conditions
Adaptation is key to thriving in a changing climate. Communities across California are already taking steps to adjust to shifting precipitation patterns. Examples include:
- Implementing green infrastructure projects to enhance urban water retention.
- Developing early warning systems for flood and drought emergencies.
- Supporting research into climate-resilient technologies and practices.
These efforts demonstrate the power of collective action in addressing complex environmental issues.
Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about California precipitation totals is crucial for fostering informed decision-making. Educating residents about the importance of water conservation and the role of precipitation in shaping the state’s environment can inspire meaningful change. Schools, community organizations, and media outlets all play vital roles in spreading this message.
Interactive tools like online dashboards and mobile apps provide users with real-time information about rainfall levels and water usage. By engaging people directly, these platforms encourage participation in water-saving initiatives and promote a culture of sustainability.
Community Engagement
Engaging communities in discussions about precipitation and water management empowers individuals to take action. Hosting workshops, hosting webinars, and organizing volunteer events are just a few ways to involve citizens in shaping the future of California’s water resources. When people feel connected to the issue, they’re more likely to support policies and programs designed to address it.
Conclusion: Taking Action for a Sustainable Future
In conclusion, California precipitation totals are a vital component of the state’s environmental and economic health. By understanding the factors influencing these totals and implementing effective management strategies, we can ensure that future generations have access to the water they need. But this isn’t just a job for scientists and policymakers—it’s a responsibility shared by everyone who calls California home.
I urge you to get involved in local efforts to promote water conservation and sustainability. Whether it’s reducing your own water usage, supporting legislation aimed at protecting natural resources, or simply learning more about the issue, every action counts. Together, we can create a brighter, wetter future for the Golden State.
Table of Contents
- Understanding California Precipitation Totals
- Factors Influencing California Precipitation Totals
- Historical Perspective on California Precipitation
- Current Trends in California Precipitation Totals
- Regional Variations in Precipitation
- Impact of Precipitation on Agriculture
- Water Management Strategies
- Climate Change and Future Projections
- Adapting to Changing Conditions
- Public Awareness and Education
- Community Engagement
Detail Author:
- Name : Anne Marquardt
- Username : deonte.jacobi
- Email : ngusikowski@gmail.com
- Birthdate : 1987-10-30
- Address : 146 Hackett Lodge Jerodville, CA 24624-0763
- Phone : 689-613-0108
- Company : Lueilwitz, Bradtke and Boehm
- Job : Operations Research Analyst
- Bio : Ab eos sit non consequatur. Atque blanditiis officiis explicabo minus. Dolor debitis dolor alias ex ut.
Socials
linkedin:
- url : https://linkedin.com/in/toy1991
- username : toy1991
- bio : Aut omnis eius magnam est.
- followers : 539
- following : 2381
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/lonny.toy
- username : lonny.toy
- bio : Rerum et dolores itaque placeat aut cumque adipisci.
- followers : 933
- following : 100