Monomer Of Carbohydrates: The Building Blocks Of Life
Carbohydrates are everywhere, and they play a crucial role in our daily lives. From the food we eat to the energy that fuels our bodies, understanding the monomer of carbohydrates is like unlocking the secret recipe of nature. These tiny molecules are the foundation of a massive biological system that keeps life on Earth running smoothly. So, what exactly are these monomers, and why should you care? Let’s dive in and explore this fascinating world together!
You’ve probably heard the term “carbohydrates” thrown around in health articles, diet plans, and even casual conversations. But have you ever stopped to think about what they’re made of? Carbohydrates aren’t just random compounds; they’re built from specific molecules called monomers. These monomers are the building blocks that form the complex structures we know as carbohydrates. Without them, life as we know it wouldn’t exist.
Now, before we get too deep into the science, let’s clarify why this matters. Whether you’re a student trying to ace your biology exam, a health enthusiast curious about nutrition, or simply someone who loves learning about the world, understanding the monomer of carbohydrates can open your eyes to how nature works. Stick around because we’re about to break it down in a way that’s easy to digest—pun intended!
What Are Carbohydrates Anyway?
Let’s start with the basics. Carbohydrates are one of the three main macronutrients that our bodies need to function properly. Alongside proteins and fats, they provide the energy we need to go about our day. But here’s the kicker—they’re not just random molecules floating around. Carbohydrates are actually polymers, which means they’re made up of smaller units called monomers.
Think of carbohydrates like a Lego tower. Each little brick in that tower is a monomer, and when you stack them together, you create something much bigger and more complex. In the case of carbohydrates, those "bricks" are sugar molecules known as monosaccharides. Yep, sugar is the star of the show here!
Types of Carbohydrates
Not all carbohydrates are created equal. They come in three main forms:
- Movierulz 2025 Latest Movies News You Need To Know
- Movierulz 2025 Latest Movies News You Need To Know.htm
- Monosaccharides: These are the simplest form of carbohydrates and serve as the building blocks for more complex structures.
- Disaccharides: When two monosaccharides join together, they form a disaccharide. Think of it like two Legos stuck together.
- Polysaccharides: These are the big guys. They’re long chains of monosaccharides linked together, forming complex structures like starch and cellulose.
So, when we talk about the monomer of carbohydrates, we’re specifically referring to monosaccharides. These little guys are the foundation of everything carbohydrate-related, and they’re super important for both plants and animals.
Monosaccharides: The Real MVPs
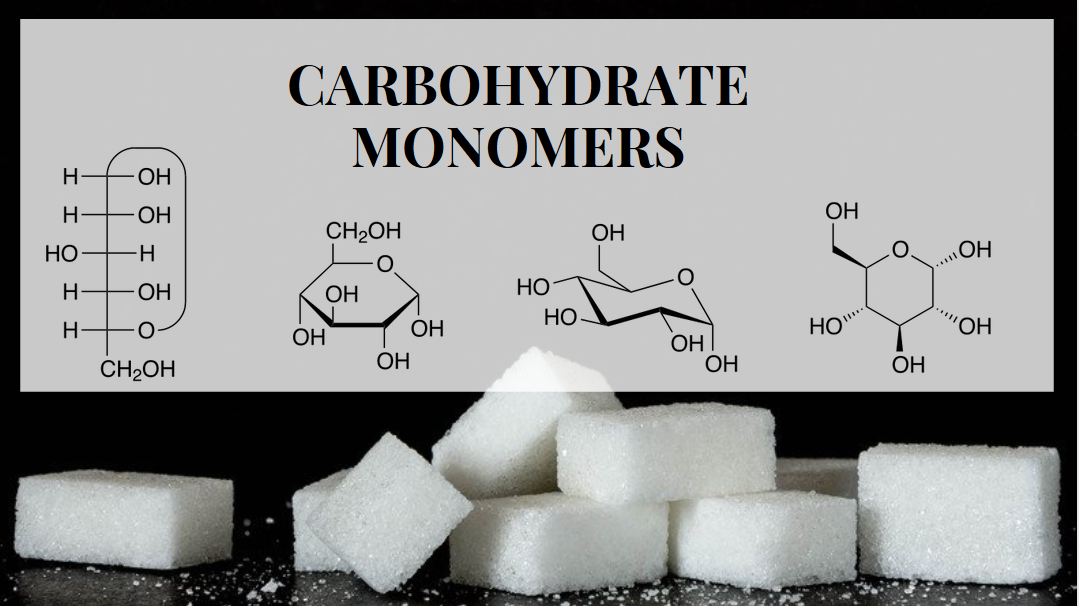
Alright, let’s zoom in on monosaccharides. These are the simplest form of carbohydrates and are often referred to as simple sugars. They’re made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, and their general formula is (CH₂O)n. The most common monosaccharides you’ll encounter are glucose, fructose, and galactose.
Glucose, in particular, is like the rockstar of the monosaccharide world. It’s the primary source of energy for most living organisms, including humans. Every time you eat a piece of bread or sip on a glass of juice, your body breaks it down into glucose, which is then used to power your cells.
Structure of Monosaccharides
Monosaccharides have a pretty cool structure. They can exist in either a linear or ring form, depending on the conditions. In their linear form, they look like a chain of carbon atoms with hydroxyl (-OH) groups attached. When they form a ring, they create a cyclic structure that’s more stable and commonly found in nature.
Here’s a fun fact: the ring form of glucose is actually what gives honey its sweetness. Nature is wild, right?
Functions of Monosaccharides in the Body
Monosaccharides do more than just taste sweet. They play a vital role in maintaining the health and function of your body. Here are some of their key functions:
- Energy Production: Glucose is the primary source of energy for your cells. It’s broken down through a process called cellular respiration to produce ATP, the energy currency of the body.
- Cellular Communication: Monosaccharides are involved in signaling pathways that help cells communicate with each other. This is crucial for processes like immune response and tissue repair.
- Structural Support: Some monosaccharides, like N-acetylglucosamine, are used to build structural components of cells, such as glycoproteins and glycolipids.
Without monosaccharides, your body wouldn’t be able to function properly. They’re like the unsung heroes of the biological world, doing all the heavy lifting behind the scenes.
Monosaccharides in Nature
Monosaccharides aren’t just found in the human body—they’re everywhere in nature. Plants use them to store energy in the form of starch, while insects use them to build chitin, a tough material that forms their exoskeletons. Even the cellulose in tree trunks and plant stems is made up of long chains of glucose molecules.
Here’s a breakdown of where you’ll find monosaccharides in nature:
- Fruits: Fructose is the main sugar found in fruits like apples, bananas, and strawberries.
- Honey: A mix of glucose and fructose makes honey one of the sweetest natural substances.
- Dairy Products: Galactose is a component of lactose, the sugar found in milk and other dairy products.
So, the next time you bite into a juicy apple or drizzle honey over your toast, remember that you’re consuming some of nature’s finest monosaccharides!
Monomer of Carbohydrates: Beyond Sugar
While monosaccharides are often associated with sweetness, they’re so much more than just sugar. They’re the building blocks of complex carbohydrates, which are essential for energy storage and structural support in living organisms.
For example, starch is a polysaccharide made up of glucose molecules linked together. It’s the primary way plants store energy, and it’s what gives grains like rice and wheat their nutritional value. Similarly, cellulose is another polysaccharide made from glucose, but instead of being used for energy, it provides structural support to plant cells.
Monosaccharides in Medicine
Monosaccharides also have applications in medicine. For instance, glucose is used in intravenous solutions to provide energy to patients who can’t eat. Fructose is sometimes used as a sweetener for people with diabetes because it doesn’t cause a rapid spike in blood sugar levels.
Even more fascinating is the role of monosaccharides in glycosylation, a process where sugars are attached to proteins and lipids. This plays a critical role in everything from blood type determination to the immune system’s ability to recognize foreign invaders.
Monosaccharides and Nutrition
When it comes to nutrition, monosaccharides are a hot topic. They’re often at the center of debates about healthy eating and weight management. While they’re essential for energy production, consuming too much sugar can lead to health problems like obesity, diabetes, and heart disease.
Here’s the deal: not all sugars are created equal. Natural sources of monosaccharides, like fruits and vegetables, come packaged with fiber, vitamins, and minerals that help your body process them more effectively. On the other hand, refined sugars found in processed foods lack these beneficial nutrients and can wreak havoc on your health if consumed in excess.
How to Balance Your Sugar Intake
So, how do you strike a balance between getting enough monosaccharides for energy and avoiding the negative effects of excessive sugar consumption? Here are a few tips:
- Eat Whole Foods: Focus on fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, which provide natural sugars along with fiber and nutrients.
- Limit Processed Foods: Cut back on sugary snacks, sodas, and desserts that are high in refined sugars.
- Read Labels: Be mindful of hidden sugars in packaged foods by checking the nutrition labels.
By making smart choices, you can enjoy the benefits of monosaccharides without compromising your health.
Monomer of Carbohydrates: The Science Behind It
Now, let’s get a little more scientific. The chemistry of monosaccharides is fascinating. They’re classified based on the number of carbon atoms they contain, with the most common ones being trioses (3 carbons), pentoses (5 carbons), and hexoses (6 carbons). Glucose, for example, is a hexose because it has six carbon atoms.
Monosaccharides can also be classified as aldoses or ketoses, depending on the position of their carbonyl group. Aldoses have an aldehyde group at the end of the molecule, while ketoses have a ketone group in the middle. This distinction is important because it affects how the molecule behaves in chemical reactions.
Enzymes and Monosaccharides
Enzymes play a crucial role in breaking down complex carbohydrates into monosaccharides. For example, the enzyme amylase breaks down starch into maltose, which is then further broken down into glucose by another enzyme called maltase. This process allows your body to access the energy stored in the carbohydrates you eat.
Without enzymes, your body wouldn’t be able to digest carbohydrates efficiently, and you’d miss out on a major source of fuel.
Monosaccharides in Industry
Monosaccharides aren’t just important in biology—they also have applications in industry. For example, glucose is used in the production of ethanol through fermentation, which is a key component of biofuels. Fructose is used as a sweetener in the food industry, and galactose is used in the production of infant formula.
In addition, monosaccharides are used in the pharmaceutical industry to create medications and supplements. They’re also used in the production of biodegradable plastics, which are becoming increasingly important as we strive to reduce our environmental impact.
Future Applications
As research into monosaccharides continues, we’re likely to see even more innovative applications in the future. Scientists are exploring ways to use monosaccharides in everything from renewable energy sources to advanced medical treatments. Who knows? Maybe one day we’ll be powering our cars with sugar!
Conclusion: Why Monosaccharides Matter
In conclusion, the monomer of carbohydrates—monosaccharides—are the building blocks of life. They provide energy, support cellular communication, and play a vital role in both nature and industry. Whether you’re fueling your body with glucose or marveling at the complexity of cellular processes, monosaccharides are always hard at work behind the scenes.
So, the next time you enjoy a sweet treat or marvel at the beauty of nature, take a moment to appreciate the tiny molecules that make it all possible. And if you’ve learned something new today, don’t forget to share this article with your friends and family. Together, let’s spread the word about the incredible world of monosaccharides!
Table of Contents
- What Are Carbohydrates Anyway?
- Monosaccharides: The Real MVPs
- Functions of Monosaccharides in the Body
- Monosaccharides in Nature
- Monomer of Carbohydrates: Beyond Sugar
- Monosaccharides in Medicine
- Monosaccharides and Nutrition
- Monomer of Carbohydrates: The Science Behind It
- Monosaccharides in Industry
- Conclusion: Why Monosaccharides Matter


Detail Author:
- Name : Branson Medhurst
- Username : wolff.meghan
- Email : tiara12@mclaughlin.com
- Birthdate : 1989-04-16
- Address : 7999 Wintheiser Grove Casperhaven, KS 55090-8533
- Phone : 603.383.4665
- Company : Becker LLC
- Job : Physician Assistant
- Bio : Illum maiores unde assumenda perferendis veniam. Occaecati architecto molestiae et recusandae itaque. Reprehenderit omnis fugit dolorum blanditiis et illum et. Labore qui et dicta ipsa.
Socials
instagram:
- url : https://instagram.com/ayden1727
- username : ayden1727
- bio : Et iure nemo possimus. Nihil ut ducimus tempora. Explicabo harum incidunt beatae vel.
- followers : 1402
- following : 937
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/aydenschumm
- username : aydenschumm
- bio : Dolores autem quis deserunt vel saepe sit quia. Odit laboriosam iure fuga.
- followers : 3662
- following : 843